World War 2 History, Summary
World War II (1939-1945) is the most extensive and bloodiest conflict in human history to date. During the war, between 50 and 60 million people lost their lives, of which about 13 million in the Holocaust .
World War II involved several small and large conflicts fought in different parts of the world. On one side stood the Axis powers, which consisted primarily of Germany , Italy and Japan . The other side consisted of the Allies, who were mainly Britain , France , the Soviet Union and the United States .
The prelude to the Holocaust
In interwar Germany, Adolf Hitler was able to use the recession to strengthen his power. He turned to the economically vulnerable groups in German society and blamed the scapegoats instead of pointing to the recession. Nazi election propaganda also exploited the widespread communist terror. Adolf Hitler was portrayed as the savior and the only alternative before the Communists.
In 1933, the Nazis were able to take power in Germany with Adolf Hitler as leader. Hitler immediately set about equipping Germany for war. At the same time, Nazi discrimination and persecution of Jews and other ethnic groups from which they distanced themselves increased.
First, they tried to get the Jews to flee or emigrate (emigrate) to other countries. But it was difficult because many countries did not accept Jewish refugees . The Jews who did not leave the country eventually ended up in labor camps and concentration camps .
The persecution of Jews and other designated ethnic groups would later escalate into a well-organized genocide.
Hitler expands Germany’s borders and concludes a pact with Stalin
In the mid-1930s, Hitler began to demand that various German-dominated areas around Germany’s borders be united with the “German core country” in order to create a Greater Germany. 1938 was annexed (incorporated) Austria and soon afterwards marched German troops into Sudetområdena (which is largely inhabited by German speakers), Czechoslovakia (today’s Czech Republic and Slovakia ).
Also Interesting to Read: World War I History, amazing facts
Britain and France were initially passive but eventually promised to help Poland if attacked. The Allies also expected the Soviet Union to stand in the way of a German attack on Poland. It therefore became a cold shower for the Allies when Germany and the Soviet Union concluded a pact in 1939. According to the agreement in the so-called Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact, Poland was to be divided between the two great powers. The Soviet Union was also promised free rein in the Baltics ( Estonia , Latvia , Lithuania ) and Finland .
Hitler’s goal
Hitler’s first goal was to regain the territories lost in connection with the Peace of Versailles after the First World War and to unite all German-speaking peoples in one kingdom. Thereafter, the territory of Germany was to be extended to the east to create habitats for the German people . The logical goal of the latter was to seize the large natural resources that existed in the east and thereby make Germany self-sufficient in many important raw materials such as. oil. Hitler therefore had plans from the beginning to attack the Soviet Union.
But before the great attack on the Soviet Union, Poland would first be incorporated into the German Empire. By conquering Poland, Hitler intended to create a free passage to German-owned East Prussia, which lay some distance to the east and had been separated from Germany since the Peace of Versailles (see map on the right). At the same time, the German armed forces would have an important area of march ahead of the planned attack on the Soviet Union. Hitler took advantage of the fact that many Germans wanted to reunite the “lost” East Prussia with the German core country and that Poland was in the way.
After the conquest of Poland, the German armed forces would attack to the west, including against France to get their backs free (both Britain and France had promised to help Poland if the country was attacked by Germany). Not until this was clear would the East be conquered. The German military leadership thus wanted to avoid getting caught up in a multi-front war as during the First World War.
When did World War 2 begins and ended?
On September 1, 1939, Germany launched its offensive against Poland . A few days later, Britain and France declared war on Germany. World War 2 had begun.
At the outbreak of the war, the German army was a well-equipped and efficient war machine drilled in modern warfare. To avoid ending up in a sluggish war of position as during the First World War, ” lightning war ” was applied . The blitzkrieg was to soften the enemy by bombing strategic positions. Then tanks were used to break the enemy’s lines. Finally, the infantry came and cleared away any remaining resistance.
Also Read: Major Battles of the World War I
The Soviet Union found it difficult to keep up after the German ally’s lightning attack on Poland. The Red Army was thrown into Poland, which had already been virtually defeated by the Germans. When Poland capitulated, the country was divided between the Soviet Union and Germany under the current Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact.
On November 30, 1939, Finland was attacked by the Soviet Union. The Finnish army offered stubborn resistance for three long winter months , but was eventually forced to surrender to the Red Army.
1940 – Country after country is occupied by the German armed forces
On April 9, 1940, the German army attacked Denmark and Norway . In this way, Germany wanted to acquire protected submarine bases in the deep Norwegian fjords, but even more important was to secure the important iron ore supply from Sweden to Germany that went via Narvik in northern Norway.
On May 10, the German army attacked the Netherlands , Belgium and Luxembourg to reach France . A few weeks later it was France’s turn. Britain had previously sent over a large expeditionary force (a smaller army) to help France in the event of an attack. But both the British and the French were ill-prepared for the German blitzkrieg tactics. The French army was soon forced to retreat, after which the British evacuated their remaining forces via the French port city of Dunkirk.
Also Interesting: Vietnam War History
On June 14, Paris was occupied by German troops, and on June 22, a ceasefire was signed between France and Germany.
The Germans divided France into two zones for better control. Northern France was occupied by German troops and the southern part of the country came to be ruled by an appointed German-friendly puppet government, the so-called Vichy regime.
Hitler is the winner in the West … only Britain remains
In June 1940, the German Armed Forces emerged victorious in the West. The back was almost free. All that remained now was to make peace with Britain. But Britain refused . Hitler therefore had no choice but to try to subjugate the dictatorial island nation by force.
The German military leadership knew they were not in control of the British navy. A direct invasion of the island was therefore not possible. Germany, on the other hand, had a very large and state-of-the-art air force – the Luftwaffe. Hermann Göring , who was Hitler’s closest man and commander of the German air force, promised to quickly force the British to the negotiating table.
Britain would be bombed to submission
The Battle of Britain began in August 1940. However, the German air raids became very costly for the Luftwaffe, which suffered heavy losses. The British had, among other things, better fighter planes (mainly Spitfire) and an efficient radar system that could detect where the Germans would strike.
Hitler eventually had to give up the invasion plans. In May 1941, the last units of the Luftwaffe were withdrawn from the area to be used instead in the long-planned attack on the Soviet Union.
The attempt to get Britain to withdraw from the war had failed. Like the course of events during the First World War, the German armed forces did not succeed in keeping their backs free. History seemed to repeat itself.
1941 – German military forces clean up after Italy’s failure
Mussolini’s fascist Italy , Germany’s ally, also wanted to show muscle. After declaring war on the Western Allies, Italian troops invaded Egypt in September 1940. Just over a month later, Mussolini invaded Greece to give Italy some “living space” in the east. The Italians’ war effort was a thunderous failure. Hitler was therefore forced to send military aid to clean up after the adventures of his furious ally.
Also Interesting: What Countries were Involved in World War 1
In February 1941, the German Africa Corps under Erwin Rommel arrived in North Africa, where it immediately gained the upper hand in the Desert War against the British. Shortly afterwards, the German army invaded Greece and Yugoslavia. Large German military resources thus had to be set aside in several places in the south, which Hitler probably had not expected from the beginning.
Hitler attacks the Soviet Union
On June 22, 1941, the long-planned invasion of the Soviet Union, Operation Barbarossa, began . The attack is the largest ever carried out in world history. Several million German soldiers with allies participated on a broad front.
The Soviet Union was surprised. Stalin did not expect an attack, at least not so soon. The Soviet Red Army was also ill-equipped and poorly managed due to previous clerical rallies carried out on Stalin’s orders. The Germans therefore achieved great success in the beginning. But the Russian resistance gradually hardened.
The Holocaust is intensifying
In connection with the invasion of the Soviet Union in 1941, the persecution of Jews turned into systematic annihilation.
The extermination camps were located mainly in Poland, within a comfortable distance from Germany and the German people. When they were ready to move in, European cities began to be emptied of Jews, Roma, homosexuals and opponents of the Nazi regime being transported to the camps. Those who were not fit for slave labor were killed. Children, the elderly and many of the women were often sent directly to the gas chambers.
It is estimated that up to 13 million people (of which about 6 million Jews) were murdered by the Nazis during the Holocaust .
The United States is drawn into the war
In 1941, the war spread to Asia, where the colonies of the Western powers were conquered by Japan, which was Germany’s ally in the east. Japan , like Germany, wanted to expand its territory. The only obstacle was the United States.
When the Japanese then attacked the US Pacific Fleet at Pearl Harbor , December 7, 1941, the United States was drawn into the war. Shortly afterwards, Germany and Italy also declared war on the United States. The war had now become a world war.
1942 – the great triumph of the Axis powers
In 1942, the Axis powers seemed unbeatable. Germany was victorious on all fronts while Japan conquered large parts of Southeast Asia. Nothing seemed to stop their military advance around the world.
1943 – War breaks out
It was on the eastern front that the war was decided. This was where the Germans put in almost all their resources. It was also where most fell. After a large army from the German armed forces in Russia was surrounded by the city of Stalingrad – the city was named after Stalin, the leader of the Soviet Union and therefore extra important to defend – around the turn of 1942-1943, the Red Army was able to counterattack on the eastern front . The war now began to turn in favor of the Allies.
In 1943, the Germans lost two decisive battles in Russia – first the battle of Stalingrad and then the great armored battle of Kursk.
After 1943, it was no longer just a matter of survival for the Soviet Union, now it was also a matter of revenge. In addition, Stalin had plans to create a Soviet buffer zone in Eastern Europe as a future protection against Germany.
1943 was also the year the Germans were expelled from North Africa.
After expelling the Axis powers from North Africa, the Western Allies landed in Sicily in July 1943 . Shortly afterwards, Mussolini was deposed, after which Italy passed to the Allies.
That same year, the Allies escalated the bombing war against Germany . The English and American air flotillas now made sure that the bombs fell both day and night over the German cities.
The bombings hit the German civilian population extremely hard. Entire cities were razed to the ground and more than half a million people lost their lives. The German people had to pay a high price for Hitler’s war.
1944 – The Western Allies open a front in the West
In June 1944, the Allies succeeded in landing Normandy in France. A front in the west had finally opened. The incident came to shorten the war. Hitler was thus obliged to fail to bring Britain to the negotiating table before. From now on, as in the First World War, Germany would have to fight a two-front war.
The German armed forces now had to move large forces from the eastern front to the new front in the west. It was not long after that before the German army in the east gave way completely and began to retreat towards Germany.
The United States gains an advantage over Japan in the Pacific
In 1944, the war in the Pacific had also turned in favor of the Allies. Japan could not match the enormous resources of the United States. But the Japanese military was still far from defeated.
Hitler refuses to surrender
By the end of 1944, Hitler was desperate. To get Britain out of the war, England was bombarded with Hitler’s new superweapons: V1 and V2 missiles (the forerunners of today’s short- and long-range robots). But the effect was absent. Britain continued to fight.
In a last desperate attempt to stop the Allied advance in the West, Hitler bet everything on one card – a massive surprise attack through the forested mountain range of the Ardennes in southern Belgium. The plan was to cut off the Allies’ maintenance lines to get the Western Allies to make peace with Germany. The German armed forces could then continue the war on the eastern front undisturbed.
In the Ardennes Offensive, which began in December 1944, Hitler threw in his last military reserves. But it was too late. The Allies already had too many resources and dominated the airspace with their air forces. The attack failed. Thus, Germany had used up its last opportunities to lead an organized resistance.
Hitler nevertheless forbade all Germans to capitulate. The war therefore continued for several more long months, with a huge loss of human life and material destruction as a result.
1945 – World War 2 ends … Cold War begins
By the end of March 1945, the Western Allies had crossed the Rhine and were thus in western Germany. And in mid-April, the Soviet Red Army launched its final offensive against Berlin . Two weeks later, Hitler committed suicide in a bunker located under the German Chancellery in the city. Germany surrendered shortly thereafter on May 7, 1945. The war in Europe was finally over.
However, the fighting between Japan and the United States in the Pacific continued for a few more months.
In early August 1945, the United States dropped two atomic bombs on the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki. Japan capitulated shortly thereafter, on September 2, 1945. World War 2 was finally over.
At the end of World War 2, the Soviet Union retained all territories under its control in the final stages of the war. Europe was therefore divided into two blocs of power – one democratic and capitalist in the West, and one communist in the East.
The Cold War between the two power blocs that followed then came to dominate world politics for most of the remaining 20th century.
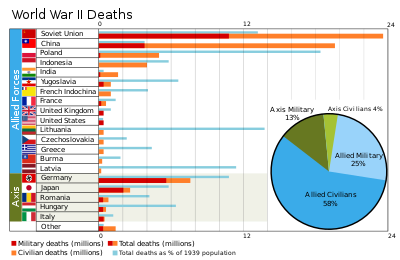
World War Causalities Graph
What are some Interesting facts about World War 2 (WW II)
Did you know that:
- World War II is the bloodiest war in history. About 56.4 million people lost their lives. The total number of dead was greatest in the then Soviet Union, which lost 26.6 million inhabitants.
- On June 4, 1940, the BBC broadcast what would become Winston Churchill’s most famous speech during World War II. It was the speech that included the words: “We will fight on the beaches.” In 1979, it was revealed that it was the British actor Norman Shelley who spoke this famous speech. On the same day, Churchill had given a speech in Parliament in London . He was supposed to repeat it on the radio, but since Churchill did not have time, actor Shelley had to imitate his voice. Churchill approved the imitation and the speech was broadcast as planned to the nation on June 4, 1940.
- The Blitz is the bombing operation carried out by the Germans from 7 September 1940 to 16 May 1941 against London and other English cities. During the attacks, 43,000 Britons were killed and the number of wounded was 139,000. About one million houses were destroyed. During the Blitz, hundreds of German bombers flew over England. But the British persevered. “Never before in the history of the peoples’ struggles have so many had so little to thank for so much,” Winston Churchill said in a famous speech.
- The last cavalry shock occurred in November 1941 when a Mongol cavalry unit attacked German troops outside Moscow. About 2,000 riders fell during the attack. No German soldiers died.
- The Germans’ most terrifying plane during World War II was the Ju-87 Stuka bomber . The plane could carry a bomb load of 1000 kg. Stukan’s victim gave it the name “The Screaming Game”. Many of these planes were equipped with sirens that howled when they dived.
- In 1942, the Nazis decided on “the final solution to the Jewish problem”, which meant that all Jews would be exterminated. The 30 largest concentration camps were supplemented by a series of extermination camps. In all, the Nazis executed about 6 million Jews.
- Auschwitz was an extermination camp built by the Germans in central Poland during World War II. About 2.5 million people were killed in Auschwitz between 1940 and 1945.
- Landing in Normandy during World War II is the largest invasion in world history. From D-Day on June 6, 1944 onwards, 1.1 million soldiers, 200,000 vehicles and 750,000 tons of supplies were landed.
- Towards the end of World War II, the Germans threatened the Allies (England and France) with a secret weapon that they would use against the Allied cities. One week after the Allied invasion of Normandy, the new rockets were ready to be fired. They came to be known as V1, which was an abbreviation of Vergeltungswaffe 1 (Retaliation Weapon 1), and were Hitler’s revenge for the Allied terror bombings of cities such as Hamburg and Berlin.
- On September 8, 1944, a weapon came that was even worse than the V1: V2 rocket, which went five times faster than the sound. Unlike V1, it was impossible to shoot down. You neither heard nor saw it. It only got smaller and then many people died. The first attacks with the V2 rockets were aimed at London and Antwerp. Before the end of the peace in May 1945, thousands of V2 rockets had gone down in London. In total, the V1 and V2 rockets claimed over 37,000 victims in a few months. However, the accuracy of the rockets was poor and the two weapons of retaliation never had any military significance that affected the outcome of the war.
- The Japanese almost never gave up when they fought. The Battle of Iwo Jima Island in the Pacific Ocean in 1945 showed that. When the United States conquered the island, 20,000 Japanese soldiers fought to the end, only 216 survived.
- In April 1945, the Red Army approached Berlin. All roads from the city were closed and Hitler decided to take his own life. He was extremely afraid of being captured by the Russians. He believed that Soviet leader Stalin would show him in a cage on Red Square. Therefore, he wrote his will and said goodbye to his closest men at a simple meal that consisted of spaghetti and salad. It was April 30, 1945. At 15.00, Adolf and Eva went into their private room together. Nobody knows what happened in the closed room. It is known that both Hitler and Eva had hydrocyanic acid capsules (Hitler had tried the hydrocyanic acid on his German Shepherd bitch Blondi) and pistols with him. Eva probably took her life with a poison capsule and Hitler shot himself in the temple with his pistol.
Useful concepts
The Axis Powers: A pact that consisted mainly of Germany, Italy and Japan.
Lightning war: A form of warfare that was used successfully by the Germans at the beginning of World War II, e.g. during the attack on Poland in 1939 and France in 1940 , but also during the Desert War in North Africa and in the initial phase of the attack on the Soviet Union in 1941.
The principles of the blitzkrieg were to attack and break through the enemy’s lines of defense with planes, tanks and other motorized troops. The remaining resistance was then cleared away by the infantry. The use of the radio was important, as it made it possible to quickly send out orders to, for example, call in combat flights.
The German military Heinz Guderian became known as the “father of the blitzkrieg” because he introduced tanks and mobile blitzkrieg-type warfare into the German army in the 1930s. The most obvious example of a successful German blitzkrieg was the attack on France, where the Germans quickly defeated allied forces based on an outdated doctrine based on the battles of the First World War.
Allied : An ally, aide, brother in arms.
The Allies: An alliance consisting mainly of Great Britain, France, the Soviet Union and the United States.
The term “allied” usually refers to when states are linked to each other by agreement. This usually means that the states promise to help each other in war.
The Holocaust: The Swedish name for the genocide that the Nazis carried out in 1933-1945 on just over six million Jews and about seven million other people. The Holocaust took place mainly in the shadow of World War II and was hidden by the war.
Living space : The concept (living space) became one of Adolf Hitler’s favorite political and agitational ideas and a cornerstone of Nazi ideology . The doctrine, which Hitler had borrowed from some other contemporary “theorists”, aimed to divide the world into so-called great spaces (grossräume) where each great power could decide. Hitler considered that the Germans in particular and the Germans in general constituted a “master people” and thus were superior to “subhumans”. Slaves (Russians, Poles, etc.) were subhumans of Nazi ideology. According to Hitler’s ideology, the lords deserved “living space” (living space) at the expense of the slaves.
Occupation: In international law and military contexts, occupation means that a state militarily occupies the territory of another state for a longer period and that the occupying state takes over all or part of the occupied state’s functions as a legal authority.
Tasks and questions
Questions to the text:
- Which states fought against each other during World War II?
- Why did Hitler attack Poland?
- Why did the Germans attack France?
- What is meant by lightning war?
- Why did the German military not succeed in invading Britain ?
- Why did Hitler attack the Soviet Union?
- What was the Holocaust?
- Why did Japan attack the United States?
- World War II was largely fought in Russia, where it was also decided. Briefly describe at least one important event that can be described as a turning point in the war.
- How did the landing of the Western Allies in France in 1944 affect Germany’s situation and the course of the war?
- How did World War II end in Europe?
- How did World War II end in Asia?
Find out:
- Briefly tell about the Winter War between the Soviet Union and Finland.
- Who were the following people:
a) Adolf Hitler
b) Winston Churchill
c) Josef Stalin
d) Benito Mussolini
- What was SS ?
- What happened during the Nuremberg trials ?