Mostly in this world people think that the war is not the batter solution for any kind of dispute, violence and misunderstanding. If we take a look on the history of this word when the war is being started, there were number of causes from which the brutality and the economic disasters were major causes that were going through the countries to countries. A number of the battles have been fought in the history of this world but the World War 1 is of the most hazardous wars that have been fought in this universe. In this historical war starting on 28th July, 1914 and ended on 11th November , 1918 many of the nations have fought and about 9 million soldiers and around 7 million civilians have died during this great and long lasting battle.
Major Causes of the WWI
The World War 1 is consisted on the number of reasons such as hostility, discrimination and conflicts that lead the world to start this war and in this war imperialism, nationalism, alliance, and militarism also took the part to this great global War. The World War 1 triggered is directly press when Austrian archduke, Franz Ferdiand and his wife were killed. Following are the major causes which were directly involved to start this great battle.
Factors Behind the Outbreak of World War 1
In our exploration of the major causes behind the outbreak of World War 1, we embark on a historical journey to unravel the intricate web of events, alliances, and tensions that ignited one of the most devastating conflicts in human history. The First World War, often referred to as the Great War, was a pivotal global event that reshaped the world in profound ways. To truly understand the origins of this colossal conflict, we must delve deep into the multifaceted factors that led to its eruption.
Imperialism: The Global Power Struggle
At the turn of the 20th century, the world witnessed an intense scramble for colonies and resources among the major European powers. Imperialism was a driving force as nations sought to expand their empires. Countries like Britain, France, Germany, and Russia competed for control over territories in Asia, Africa, and other regions. This fierce competition sowed the seeds of discord, as nations constantly jockeyed for global dominance.
Militarism: The Arms Race and Growing Tensions
Simultaneously, an ominous arms race unfolded across Europe. Militarism had taken hold as nations engaged in an aggressive buildup of their military forces. This buildup wasn’t just for defensive purposes but also as a show of strength and a deterrent to potential rivals. The belief that a formidable military was essential for national prestige and security led to an alarming proliferation of weapons, creating an atmosphere of tension and suspicion.
It is the situation when a country wants to maintain a strongest and most defending military strength. It was also the one of the major factors for starting this great battle around the globe because European and other nations stared arms race. The number of French and German soldiers doubled between 1870—1914 and there is very great competition in Britain and Germans. When British launch its battleship name “Dreadnought” in 1906 the Germans followed and introduced their own battle ship.
Alliances: The Complex Web of Relationships
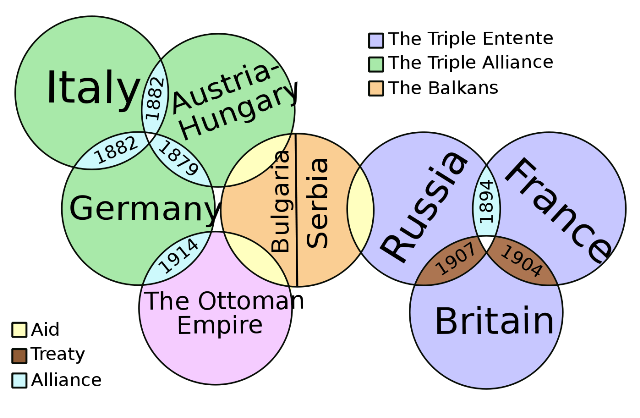
The intricate system of alliances that characterized the early 20th century added further complexity to the geopolitical landscape. Key alliances included the Triple Entente, consisting of France, Russia, and Britain, and the Triple Alliance, featuring Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy. These alliances were formed for mutual defense, but they also created a precarious situation where a conflict involving one nation could swiftly draw others into the maelstrom.
Nationalism: The Stirring of National Pride
Nationalism was on the rise, fueling fervent patriotism and a sense of national pride in many countries. This sentiment often translated into aggressive foreign policies, as nations aimed to assert their dominance and expand their borders. Nationalist fervor in the Balkans, for example, significantly contributed to the volatile atmosphere that eventually led to the outbreak of World War 1.
Assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand: The Trigger
While the underlying causes of World War 1 simmered for years, it was the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria-Hungary on June 28, 1914, in Sarajevo, Bosnia, that acted as the spark for the war. The Archduke’s assassination by a Serbian nationalist set off a chain reaction of events. Austria-Hungary’s ultimatum to Serbia, backed by Germany, resulted in a series of declarations of war that plunged Europe into chaos.
The Domino Effect: Escalation to a Global Conflict
As the conflict escalated, alliances were activated, pulling more nations into the fray and transforming what started as a regional dispute into a full-scale world war. Russia’s mobilization in support of Serbia prompted Germany’s declaration of war on Russia, drawing France into the conflict. Germany’s invasion of Belgium led to Britain’s involvement. In a matter of weeks, the world found itself embroiled in a devastating war.
Conclusion: The Complex Tapestry of Causes
In conclusion, the major causes of World War 1 are a complex tapestry of imperialism, militarism, alliances, nationalism, and the triggering event of Archduke Franz Ferdinand’s assassination. The sequence of historical events leading to this cataclysmic conflict is both intriguing and somber, reminding us of the profound impact of geopolitical decisions and the far-reaching consequences when the world teeters on the brink of war.
Do you know Which Countries Were Involved in the World War 1?
Ans : Although the World War 1 was fought between number of nations around the world which damaged the economy and lifestyle of the world yet there were some countries playing the greatest role in this great war. Following is the list of both the countries from the Victor side and the Opposition Side.
List of Countries from the Victor Side that fought in the world war 1
List of Countries from the Losing Side that fought in the world war 1
| Serial No. | Country | Capital |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Söğüt, Bursa, Adrianople,Constantinople | |
| 2. | Vienna, Budapest | |
| 3. | Berlin | |
| 4 | Bulgaria | Sofia |
What happened to the countries that lost world war I
The nations that found themselves on the losing side of World War I, primarily Germany, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire (Turkey), and Bulgaria, faced a cascade of profound changes and challenges in the war’s aftermath:
- Germany: Germany, perceived as a key instigator of the war, was handed a severe set of conditions under the Treaty of Versailles in 1919. These terms included territorial losses, military disarmament, and substantial reparations. These punitive measures inflicted economic hardships and triggered political instability within Germany, eventually contributing to the eruption of World War II.
- Austria-Hungary: Post-war, Austria-Hungary disintegrated, giving rise to separate nations such as Austria, Hungary, Czechoslovakia, and fragments that would form parts of Yugoslavia and Poland. The empire’s centuries-old existence came to an end, ushering in a new era of independent states.
- Ottoman Empire (Turkey): The Ottoman Empire also experienced dissolution, leading to the emergence of modern-day Turkey, led by Mustafa Kemal Atatürk. The empire’s territories in the Middle East and North Africa were either mandated to Allied powers or granted independence, shaping the contemporary map of the region.
- Bulgaria: Bulgaria, too, was confronted with territorial losses and reparations as stipulated in the Treaty of Neuilly-sur-Seine. It relinquished land to Greece, Romania, and Yugoslavia.
- Economic and Societal Impact: The Central Powers, as a collective, grappled with economic adversity and social transformations post-World War I. The war had exacted a heavy toll in terms of lives lost, economic resources depleted, and societal upheaval.
- Political Transformations: In several of these countries, including Germany and Austria, the post-war period was marked by political instability and governmental transitions. This tumultuous era set the stage for the ascent of authoritarian regimes and, in Germany’s case, the eventual dominance of Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party.
In summary, the countries that found themselves on the losing side of World War I had to contend with territorial losses, economic hardships, political shifts, and profound societal changes. These repercussions had far-reaching implications, shaping the course of the 20th century and influencing the geopolitical landscape of the time.
In this great and long lasting battle, different countries who taken part in this battle lost thousands of their soldiers and civilians who fought in that war. But the Russian Empire had the highest number of deaths during the WW1 . Following is a chart showing the military deaths of different countries.
Summery of the WW1 Military Deaths by Country in Percentage
Also See :
- When Did the Vietnam War Start and End
- Top 10 Countries With Largest Armies in the World
- Top 10 Countries with Most Nuclear Weapons in the World
- Interesting Facts About United States
- U.S. Economy Statistics
- What Nations are Communist Now?
- What Nations are Socialist Today
- Top 10 Nations with Highest Crime Rate
- What Nations are in Europe
- Countries That Start with D
- Is Asia a Country or Continent
- What Countries Border Germany List
- What Countries Border Syria on the Map
- 25 forbidden beautiful places that people are not allowed to visit
TheCountriesOf.Com: Spreading the authentic information across the globe collecting from govt. sites of different countries and other very reliable resources. Hopefully now you are very aware of what countries were involved in the world war 1 ?
I must say you have high quality posts here. Your website should
go viral. You need initial boost only. How to get it?
Search for; Miftolo’s tools go viral