World War II was the start of a new kind of technology that would dominate airspace: jet-powered aircraft. The Germans were the first to put the Messerschmitt Me 262 into combat, and soon the great powers followed. Here we list the first jets to be put into service.
The first jet-powered aircraft saw the light of day during World War II. Just a few days before the invasion of Poland and the outbreak of war, on August 27, 1939, the German prototype Heinkel He lifted 178 from the airport in Marienehe. The flight lasted only about eight minutes, but set the entire German aviation structure rolling.
The physicist Hans von Ohain and the engineer Ernst Heinkel, the brains behind the design of the first successful jet aircraft engine, did not understand why the management of the Reichsluftsfahrt ministry showed no interest in the groundbreaking design. They did not know that the Ministry of Aviation had already launched its own secret project under the pseudonym P. 1065.
Me 262 were mass-produced
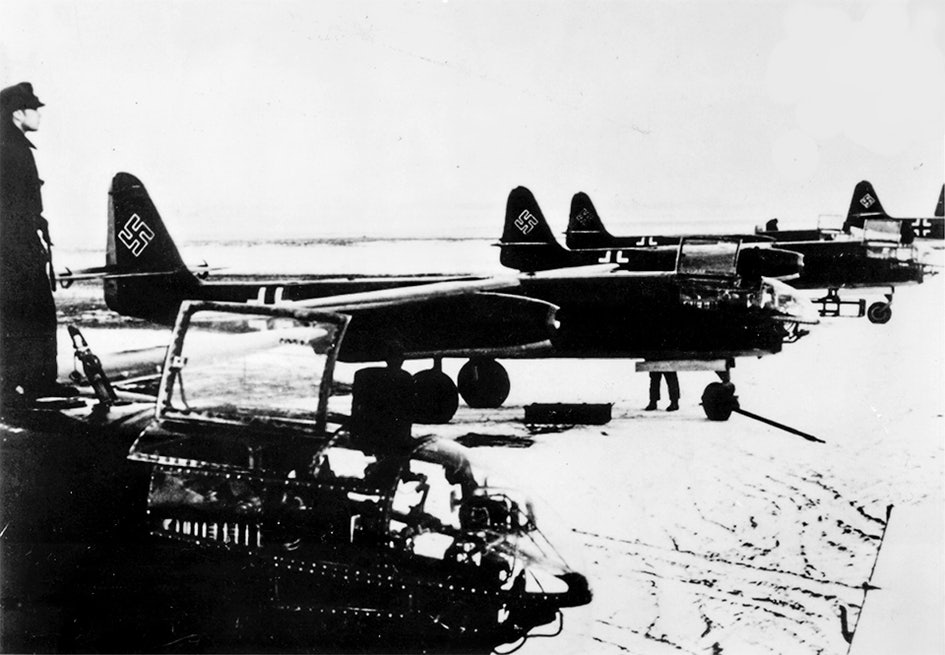
The project bore fruit in the summer of 1942, when a Messerschmitt Me 262 made its first successful flight, equipped with twin jet engines. It became the first mass-produced jet in the world, with the goal of fighting the allied propeller fighter planes Supermarine Spitfire and P-51 Mustang – both of which could reach speeds above 700 km / h.
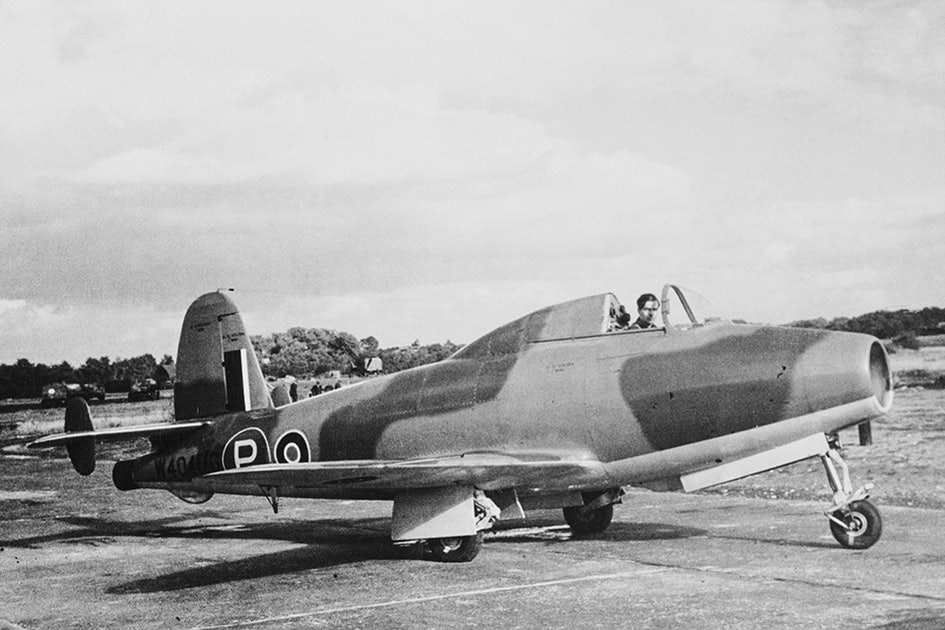
At the same time, and independent of the Germans, variants of the jet engine were invented elsewhere: among others by the Italian Secondo Campini and the British Frank Whittle. Of these, only the British jet construction was deployed during the war, in the form of the Allies’ first jet-powered fighter Gloster Meteor. It would take until the Korean War before jet planes met in air battles.
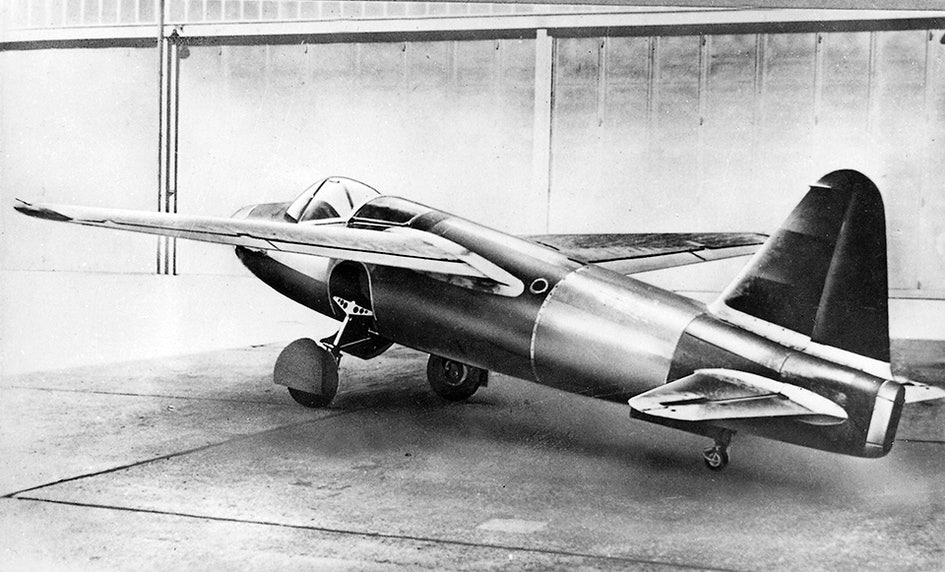
Heinkel He 178 – small pioneer was first
The world’s very first jet-powered aircraft was comparatively small and measured only 7.48 meters and weighed just over 1.6 tonnes. Hans von Ohain, who is considered one of the fathers of jet engines, had in 1936 issued a patent for using the combustion gases from a gas turbine as a propellant. Ernst Heinkel agreed to develop an aircraft with the engine.
Three years later, days before the outbreak of war, test pilot Erich Warsitz (who also flew the world’s first rocket plane) flew the maiden flight. The project had been cherished by strict secrecy and not even the Luftwaffe knew about the tests.
Also Interesting to Read: World War I Causes, History, Facts
When Heinkel presented the plane to the air force’s command in the form of Ernst Udet and Erhard Milch, they were unimpressed by the low speeds of 598 km / h and the high fuel consumption.
But Heinkel did not give up and started sketching on his own battlefield with twin engines. The result, the Heinkel He 280, became the first turbojet-powered fighter. But a combination of political and technical factors led to the model being overlooked in favor of Messerschmitt Me 262.
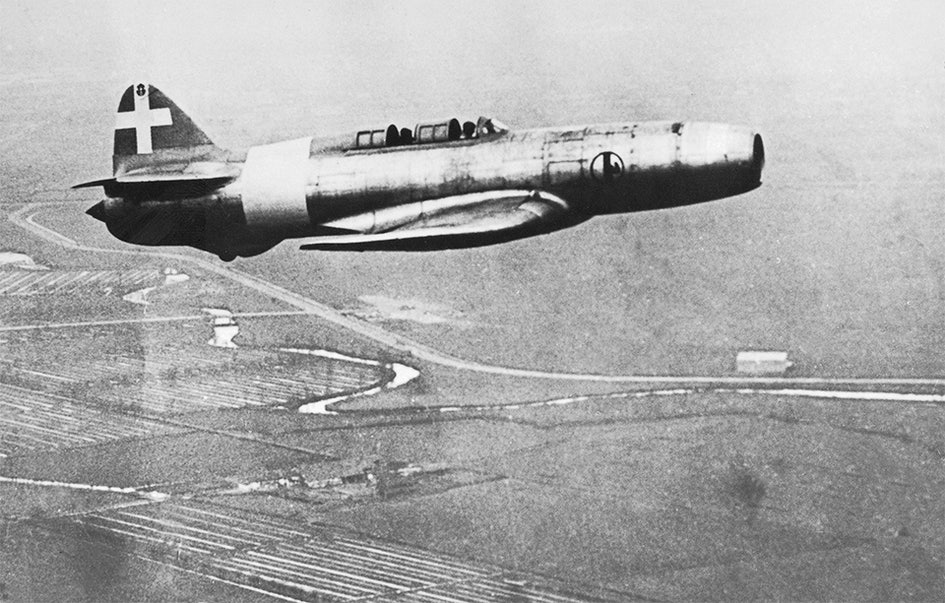
Camproni Campini N.1 – Italian propaganda
For many years it was believed that the Italians were the first in the world with a successful jet aircraft, before the German test flights a year earlier became known. On 27 August 1940, the Campini N.1 flew outside Milan with a thermojet design measuring a maximum speed of 515 km / h. However, Mussolini achieved a major propaganda victory thanks to the successful test.
Gloster Whittle – against German robot attacks
Gloster E.28 / 39 or Gloster Whittle, named after the author Frank Whittle, was equipped with the UK’s response to a turbojet engine. The patent was already under development in 1936, but it took some time before the Ministry of Air Affairs granted its support for the project and the first successful flight test was performed on 15 May 1941.
The success accelerated plans for a dual-jet fighter, and three years later lifted the prototype of the Gloster Meteor, which was later used to fight the Germans’ V-1 retaliatory weapons.
In total, the RAF shot down 14 robots during the war, but when the threat from the V-1 rockets passed, the Meteors were banned from flying over Germany so as not to risk being shot down and seized. Meteor served in the Air Force until it was phased out by more advanced models from 1956.
Arado AR 234 – the only jet bomber
On June 15, 1943, the world’s first and war’s only fully operational jet-powered bombers flew for the first time. In total, the Luftwaffe was supplied with 214 copies of the model, but the Arado Ar 234 Blitz was used mainly for air reconnaissance, and it served only to a greater extent
in the Kampfgeschwader 76 unit during the last weeks of the war.
On Christmas Eve 1944, eight Ar 234s flew to Liège in Belgium for the first bombing raids. Further efforts were mainly during the Ardennes offensive: against Antwerp, Brussels and Bastogne. Three copies were also rebuilt for night hunting. The plane could carry a bomb load of up to 1,500 kilos, but a full load lowered the maximum speed to 660 km / h and made it possible for the fastest propeller-driven enemy planes to catch up. Due to a general lack of fuel, however, the Ar 234 mostly remained on the ground in favor of other aircraft types.
The Havilland Vampire – the record planet
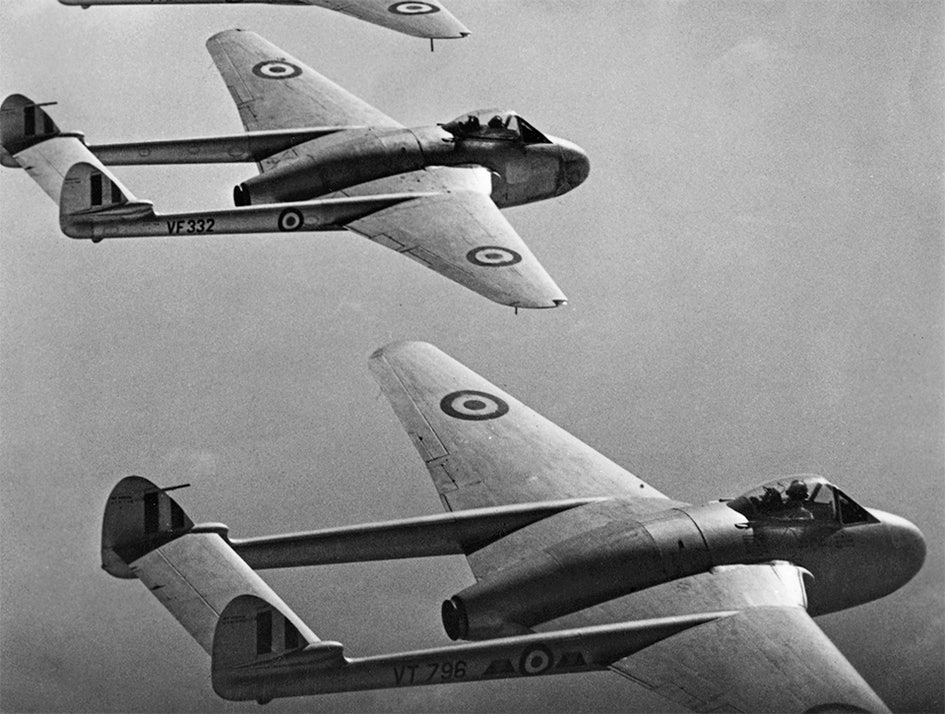

The RAF’s second jet initially flew on September 20, 1943. It was a versatile design that set several records. Double tail booms and a shortened exhaust minimized the loss of traction.
The plane was able to fly faster than 880 km / h and was, among other things, the first jet to both land on an aircraft carrier and to cross the Atlantic. Production began in the final stages of the war and only twelve copies were completed before Germany’s capitulation. Later, the plane was also adapted to the navy and was taken into the service of the British navy. The Swedish Air Force was the first foreign customer to order fighter aircraft of the type 1946, a total of 70.
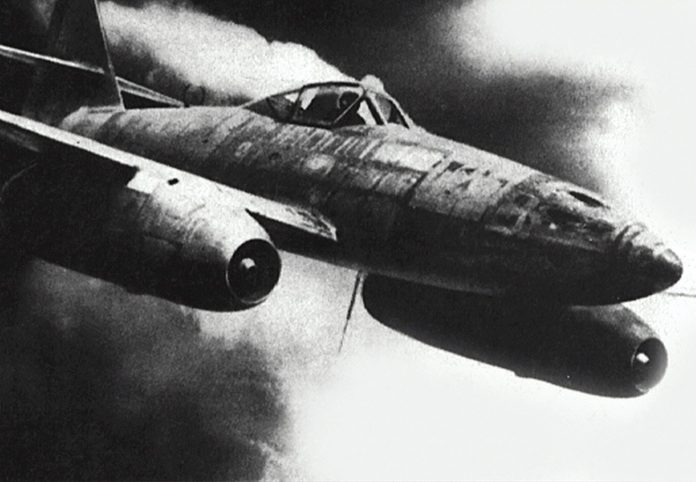
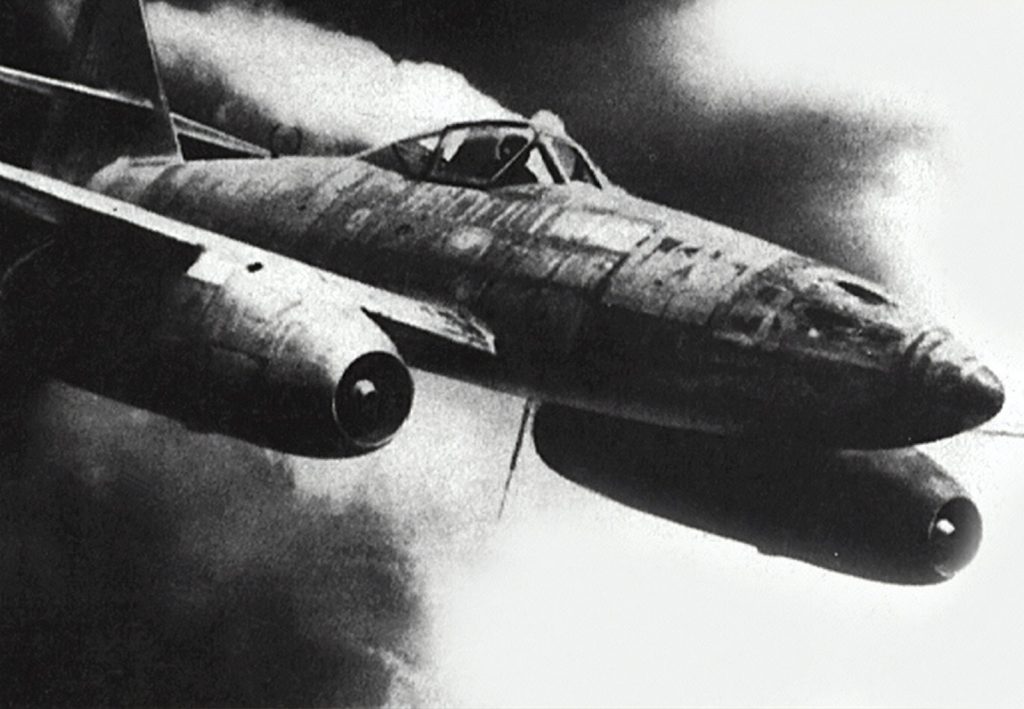
Me 262 would turn the tide of war
With the nicknames Schwalbe for the fighter version and Sturmvogel for the fighter bomber, Messerschmitt Me 262 was the very first turbojet-powered plane in combat.
The development of the first mass-produced jet-powered fighter was plagued by indecision, delays, engine problems and dubious priorities, and once the jet was deployed, the war was already lost. A jet-powered Me 262 took off on July 18, 1942, and two years later the plane was deployed.
The design of the plane was revolutionary. The arrow-shaped, backward-swept wings provided better aerodynamic conditions and higher flight speed. At the same time, the plane became vulnerable at low speeds as during takeoff and landing – not least due to inexperienced pilots. This weakness was later exploited by enemy planes.
The first sharp operation by jet plane was on July 18, 1944 when the 3rd Division of the Kampfgeschwader 51 bombed targets in France. Hitler had prioritized the production of the hunting bomb variant, in retaliation for the Allied bombing boards – despite the fact that the Me 262 worked better in the role of fighter.
The change from bomb to fighter plane also delayed production. In November 1944, series production of the hunting version began and the following spring, the Jagdgeschwader 7 became the world’s first operational jet hunting flotilla. They mainly defended German cities against Allied bombing raids. The other unit that gained access to Me 262 was Adolf Galland’s Jagdverband 44 which consisted of a flight attendant. Lieutenant Kurt Welter became Germany’s foremost jet fighter pilot with twenty confirmed shootings in the air war.
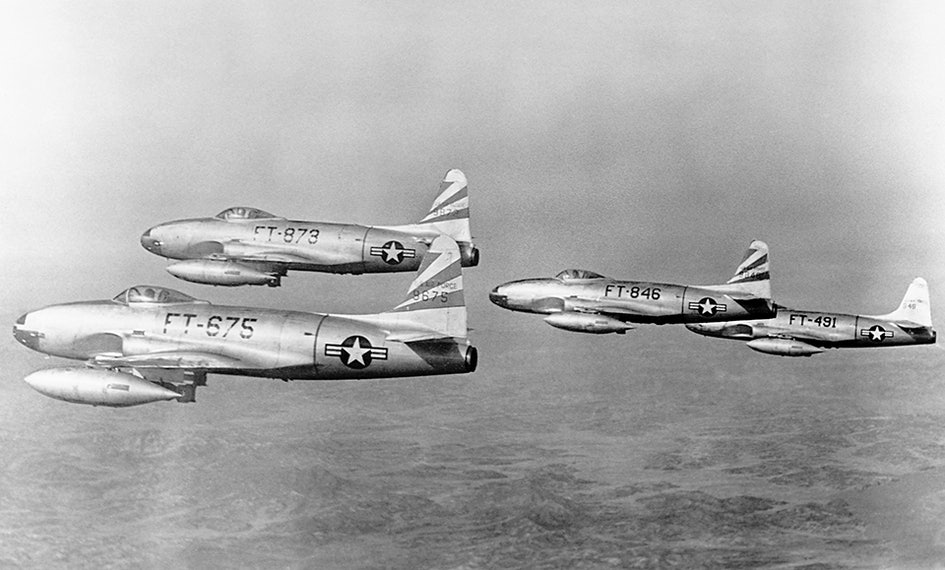
P-80 Shooting Star took the United States into the jet age
The Lockheed P-80 Shooting Star was the first successful turbojet-powered fighter in the United States. After the maiden flight on January 8, 1944, only two were put into operational service with the Air Force before the end of the war, where they performed air reconnaissance missions in Italy.
Production continued and the plane was later deployed in the Korean War. On November 1, 1950, Russian Lieutenant Chominitch went down in history as the first pilot to shoot down a Shooting Star with his MiG-15 during an air battle between jets.
Thanks for reading the article, please must share the article to give us credit !
Read More: What countries were Involved in World War I